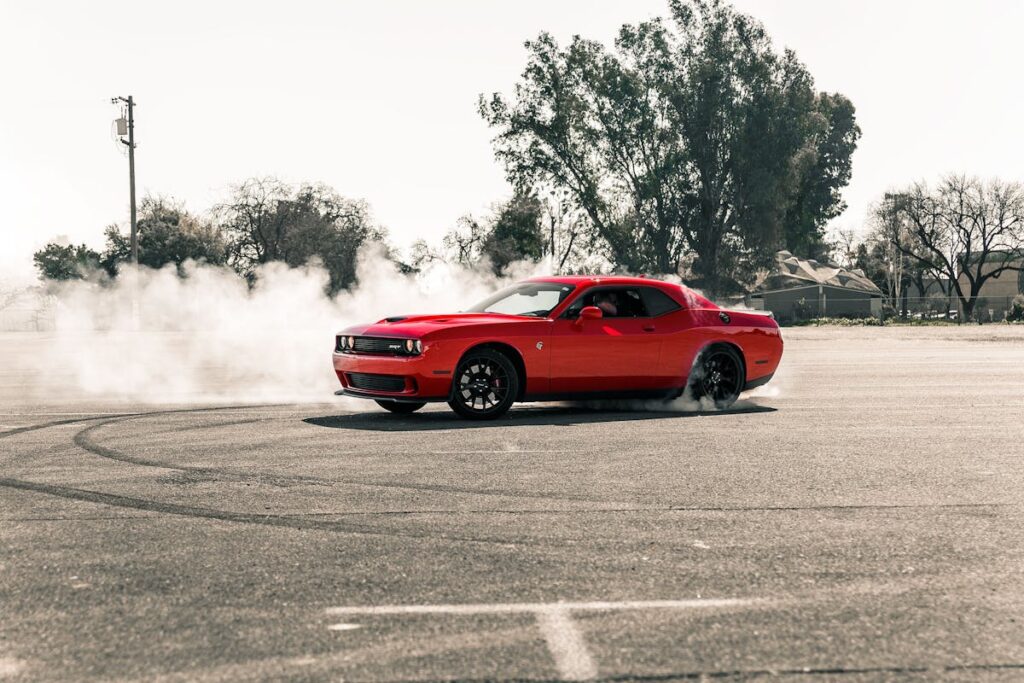
The Muscle Car Era, a dynamic period in the American automotive industry, was marked by the production of high-performance vehicles that embodied power, style, and a break from tradition. Characterized by potent V8 engines and bold designs, these cars, such as the Chevrolet Camaro and the Pontiac GTO, became cultural icons and sparked a revolution. However, this era was not without its challenges, as changing regulations and consumer preferences heralded its decline in the 1970s. Despite these setbacks, the legacy of this era still resonates today, leaving one to ponder its lasting impact and the future direction of the automotive industry.
The Birth of Muscle Cars
The advent of muscle cars marked a profound shift in the landscape of the American automobile industry. These vehicles, characterized by their powerful engines and sleek designs, emerged in the mid-1960s as a response to changing market trends. Consumers, particularly the burgeoning youth market, were increasingly seeking cars that offered not just functionality but also excitement and a sense of individuality.
Design influences played an essential role in the birth of muscle cars. Manufacturers took cues from the styles of European sports cars, marrying these with the raw power of large, American-made V8 engines. The result was a unique blending of style and performance that would come to define the muscle car genre.
This period also witnessed an intense competition among manufacturers, each vying to outdo the other regarding power, speed, and aesthetic appeal. This competition, in turn, spurred innovation and led to the production of some of the most iconic vehicles in automotive history.
The birth of muscle cars was indeed a transformative period in the American automobile industry. It reflected not just changing market trends, but also a shift in American culture towards a more adventurous and individualistic spirit.
Iconic Models of the 1960s
With the stage set by an industry-wide shift towards performance and individuality, several iconic muscle car models emerged during the 1960s that would forever leave their mark on American automobile history.
Classic competitors like the Chevrolet Camaro and Pontiac GTO, each with their unique design philosophies and engine specifications, battled for market dominance. The Camaro, with its high-performance, large-displacement V8 engine, embodied Detroit’s commitment to power. The GTO, on the other hand, emphasized balance and handling, featuring a smaller but well-tuned V8.
Cultural significance of these models was tremendous. They symbolized the rebellious spirit of the ’60s, becoming symbols of freedom and power. Performance metrics, including 0-60 times and quarter-mile speeds, became common parlance, influencing sales trends considerably.
Aftermarket modifications further fueled the muscle car craze, allowing owners to personalize their rides and extract even more performance. This, in turn, escalated collector values, making these models highly prized today.
The 1960s were a golden era for muscle cars, and the iconic models from this period continue to captivate enthusiasts worldwide. Their impact on the car industry and American culture is immeasurable, and their legacy continues to thrive.
Technological Advancements in Muscle Cars
As we shift from the iconic models of the 1960s, it is essential to analyze the technological advancements that led to the evolution of muscle cars. This discussion primarily focuses on two pivotal aspects: engine enhancement innovations and aerodynamic design breakthroughs. By understanding these strides in technology, we can gain an all-encompassing understanding of the muscle car era’s engineering prowess and sophistication.
Engine Enhancement Innovations
In the domain of muscle cars, few developments have been as transformative as the innovations in engine enhancement. Engine tuning evolved from a simple mechanical adjustment to a sophisticated science involving computerization advancements, enabling more horsepower boosts and fuel efficiency. Performance upgrades became a norm as muscle car enthusiasts sought to maximize their engines’ power output, often through aftermarket modifications.
The introduction of supercharger systems revolutionized the muscle car scene by considerably increasing horsepower and torque. These systems forced more air into the engine’s combustion chamber, leading to more powerful explosions and, as a result, more power. Exhaust enhancements, on the other hand, improved engine longevity by reducing backpressure and heat buildup, essential for maintaining peak engine performance over time.
Advancements in sound design enhanced the visceral experience of driving a muscle car, with exhaust notes tuned to deliver a satisfying rumble that underscored the raw power under the hood. Despite the focus on power, fuel efficiency was not neglected. Innovations like variable valve timing and direct fuel injection helped muscle cars extract more power from every drop of fuel, aptly demonstrating that brute strength and efficiency can coexist.
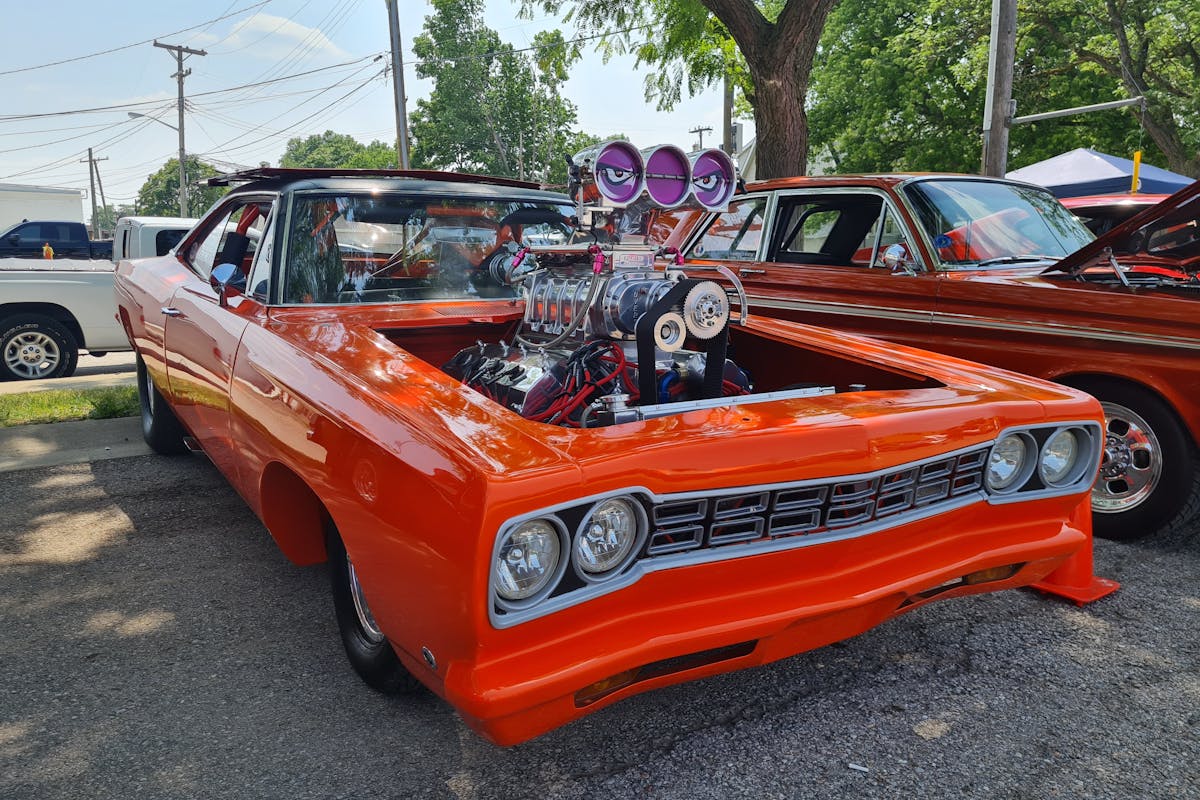

Aerodynamic Design Breakthroughs
Beyond the roaring engines and raw power, technological advancements in the aerodynamics of muscle cars have played a significant role in their evolution. Muscle car manufacturers recognized the importance of aerodynamic efficiency early on, leading to design breakthroughs that improved performance while also enhancing design aesthetics.
- Drag Reduction: Early muscle cars were boxy, a design that created significant drag. However, manufacturers strove to streamline the body design, reducing wind resistance and enhancing speed. The Dodge Charger Daytona, with its iconic nose cone and rear wing, is a notable example of this evolution.
- Weight Distribution: Proportionate weight distribution leads to better handling at high speeds. Muscle cars of the 60s and 70s incorporated technology to adjust weight distribution, improving their cornering ability and stability.
- Ventilation: Hood scoops, a common feature in muscle cars, were initially for aesthetic appeal but soon became functional. They allowed for better engine cooling and increased intake of air, which improved engine performance.
These advancements show how a blend of aerodynamic efficiency and design aesthetics have shaped muscle cars, making them more than just ‘muscle’, but also marvels of design and engineering.
The Role of Racing in Popularity
Often, the surge in muscle car popularity during the mid-20th century can be directly attributed to their prominent role in racing. This phenomenon was deeply entrenched in the racing heritage of these vehicles, which were designed and built for speed. The competitive spirit inherent in racing was a major draw for muscle car enthusiasts, with the power and performance of these vehicles setting new performance benchmarks on the track.
The fan culture around racing was another key factor. Track events were not just about the cars and drivers, but about the community that gathered to cheer them on. This grassroots movement was a demonstration to the appeal of muscle cars, and their reputation was further enhanced by the legends of drivers who skillfully maneuvered them in high stakes races.
Moreover, the sponsorship influence played a significant role in promoting muscle cars. Sponsors capitalized on the popularity of these events, associating their brands with the thrilling speed and power of muscle cars. This not only enhanced the image of muscle cars as symbols of power and speed, but also firmly established them in the public consciousness as icons of an era defined by the thrill of racing.
Impact on Popular Culture
The muscle car era’s influence permeated deeply into popular culture, leaving an indelible mark that remains evident today. This period, saturated with high-performance, aggressively styled vehicles, is a reflection of the power of cultural symbolism and automotive nostalgia.
- Film and Television: Muscle cars became icons in the entertainment industry. The 1968 film “Bullitt”, for instance, featured a memorable car chase with a Ford Mustang GT, which became synonymous with the genre. Similarly, television series like “The Dukes of Hazzard” relied heavily on the appeal of the Dodge Charger, or “General Lee”.
- Music: Musicians, particularly in the rock and roll genre, often referenced muscle cars, further cementing their cultural symbolism. The Beach Boys’ song “409” glorified Chevrolet’s powerful engine, while Wilson Pickett’s “Mustang Sally” romanticized Ford’s iconic muscle car.
- Lifestyle and Image: The muscle car era had a profound impact on fashion and lifestyle, with the powerful, sleek vehicles symbolizing freedom, rebellion, and high-octane excitement. The cars were more than just transportation. They represented a lifestyle, an attitude, and a distinctly American form of automotive nostalgia.
This cultural impact has preserved the enduring popularity and iconic status of these vehicles, long after the peak of the muscle car era.
The End of the Muscle Car Era
While the muscle car era had left an indelible mark on popular culture, it was not destined to last forever. As the 1970s dawned, a series of factors led to the gradual decline of these automotive beasts. Declining sales were the most immediate indication of changing times, closely tied to shifting demographics and evolving consumer preferences. Performance standards, once the lifeblood of muscle cars, became less significant as safety features and fuel economy took precedence in consumers’ minds.
Environmental regulations played a major role in the downfall, as stricter emission norms made it challenging for manufacturers to keep up without sacrificing power. Modern competition emerged in the form of smaller, more economical cars that catered to a more environmentally-conscious market segment. Consumer interest began leaning towards electric alternatives, which promised cleaner emissions and improved fuel economy.
However, the end of the muscle car era did not signify the end of their influence. The nostalgia factor kept the love for these vehicles alive, albeit with a diminished presence. Nevertheless, the era’s closure represented a significant shift in the automotive industry, demonstrating the impermanence of even the most iconic trends.
Revival in the 21st Century
Despite the waning of the muscle car era, the 21st century brought about an unexpected resurgence. This revival can be attributed to a handful of key factors:
- Nostalgic Appeal: Modern muscle cars imbue a nostalgic appeal, successfully rekindling interest among car enthusiasts and collectors alike. This appeal, blended with the demands of contemporary design evolution, led to the rebirth of iconic models with a modern twist.
- Electric Performance: With environmental impact becoming a significant concern, muscle cars have evolved to incorporate electric performance. This has not only expanded their appeal to global markets but also aligned them with the emerging trend of performance tuning, resulting in cars that are not only powerful but also sustainable.
- Collector Trends: The value of muscle cars has seen a steady increase due to collector trends, with many classic models becoming highly sought-after commodities. This trend has been driven by both the scarcity of original models and the desire for modern recreations that capture the spirit of the original while incorporating modern amenities.
Future Prospects of Muscle Cars
Looking ahead, the future prospects of muscle cars present an intriguing blend of opportunities and challenges. The advent of electric muscle and hybrid performance technologies is revolutionizing the landscape of muscle cars. These cutting-edge technologies are set to redefine the traditional perceptions associated with muscle cars, previously dominated by petrol-powered engines.
The shift towards electric muscle cars opens up new avenues for performance and sustainability. Electric vehicles are capable of producing instant torque, potentially enabling faster acceleration than their gasoline counterparts. Additionally, the rise in environmental consciousness among consumers has led to increased demand for sustainable vehicles, a trend that muscle cars can capitalize on by adopting hybrid performance technologies.
However, the change to electric and hybrid muscle cars is not without its challenges. The distinct roaring sound of a traditional muscle car engine is a significant part of its identity and appeal. Furthermore, the high torque associated with electric powertrains can pose handling challenges, requiring innovative engineering solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some Popular Movies Featuring Muscle Cars?
Several classic films prominently feature iconic models of muscle cars. Popular examples include “Bullitt”, “Vanishing Point”, “Gone in 60 Seconds”, and the “Fast and Furious” series, all of which showcase these high-performance vehicles.
How Do Muscle Cars Compare to Sports Cars in Performance and Design?
Muscle cars and sports cars differ greatly in performance metrics and design aesthetics. Muscle cars showcase raw power, while sports cars focus on agility and speed. Design-wise, muscle cars have a more robust and aggressive appearance.
Are There Any Notable Women Involved in the Muscle Car Era?
Yes, numerous women were notable figures during this period, such as female racers and automotive pioneers like Shirley Muldowney and Denise McCluggage, who greatly impacted the auto industry through their exceptional driving skills and innovative approaches to car design.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Muscle Cars?
Muscle cars, due to their high-performance engines, often have lower fuel efficiency and produce more emissions, consequently contributing considerably to environmental pollution. This raises concerns in light of increasingly stringent emissions regulations globally.
How Do Muscle Cars Influence the Design of Modern Electric Vehicles?
Muscle cars have notably influenced modern electric vehicles, particularly in design trends and performance features. Their aggressive styling and power-centric focus have inspired electric car manufacturers to prioritize both aesthetics and high-performance capabilities in their designs.