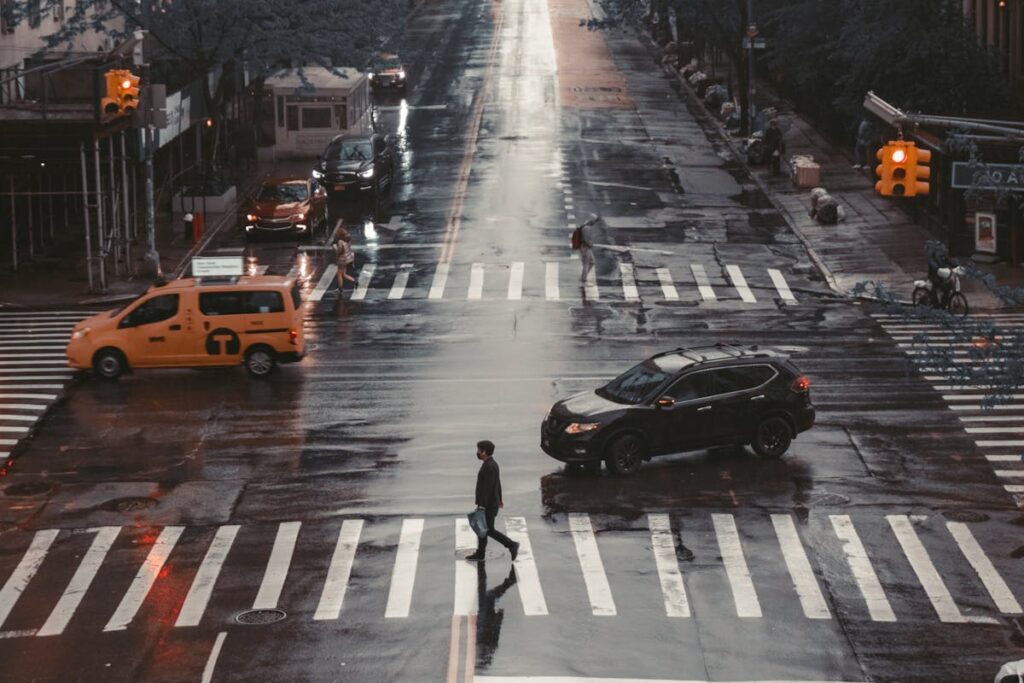
The introduction of pedestrian-friendly roads and crosswalks marks a transformative phase in urban design, focusing on safety and accessibility. By integrating features like raised crosswalks and curb extensions, cities aim to reduce vehicle speeds and accident risks. Such initiatives not only enhance pedestrian movement but also enrich community interaction and promote healthier lifestyles. This approach raises questions about the broader impacts on urban ecosystems and how these changes will shape future cityscapes.
The Rise of Walkable Cities
As urban centers evolve, there is an increasing emphasis on developing walkable cities, driven by the interconnected benefits of improved public health, environmental sustainability, and economic importance. This paradigm shift places a spotlight on urban aesthetics and the strategic design of pedestrian pathways. Cities across the globe are reimagining their landscapes to prioritize foot traffic over vehicular dominance. Urban planners are meticulously crafting environments where pedestrian pathways are seamlessly integrated into the cityscape, enhancing both functionality and visual appeal. Such designs not only cater to the needs of pedestrians but also contribute to the city’s overall aesthetic, creating vibrant, accessible spaces. These changes reflect a visionary approach, aiming to transform traditional urban environments into dynamic locales that foster community interaction and connectivity.
Benefits of Pedestrian-Centric Urban Design
Pedestrian-centric urban design offers significant advantages by fostering improved public health through increased opportunities for physical activity and reduced reliance on vehicles. By prioritizing walkability, such environments facilitate enhanced community interaction, encouraging social cohesion and vibrant local economies. Additionally, the reduction in vehicular traffic directly contributes to decreased pollution levels, resulting in cleaner air and a more sustainable urban ecosystem.
Improved Public Health
By prioritizing pedestrian-centric urban design, cities can greatly enhance public health outcomes. Encouraging walking habits through well-planned sidewalks and crosswalks leads to significant health benefits such as reduced obesity rates, lower blood pressure, and improved cardiovascular health. Walking, as a primary mode of transport, allows individuals to integrate physical activity seamlessly into their daily routines, fostering a healthier population. Additionally, pedestrian-friendly infrastructure reduces reliance on vehicular transport, thereby lowering air pollution levels, which is essential for respiratory health. The visionary approach of designing cities around pedestrians rather than vehicles also minimizes noise pollution, contributing to improved mental well-being. By systematically embedding active transportation into urban environments, cities set a foundation for sustainable, health-oriented living, making public health a cornerstone of urban planning.
Enhanced Community Interaction
Integrating pedestrian-friendly features into urban design not only fosters public health but also greatly enhances community interaction. By prioritizing pedestrian zones, cities can transform streets into vibrant social spaces where residents engage in meaningful exchanges. These areas encourage impromptu community gatherings, fostering a sense of belonging and enhancing social cohesion. The presence of pedestrian-centric zones facilitates the creation of public spaces designed for leisure and interaction, such as plazas, parks, and open-air markets. These environments naturally stimulate social interaction, enabling diverse groups to connect in informal settings. Additionally, pedestrian-friendly spaces can host cultural events, markets, and performances, further enriching community life. Such spaces contribute to a more inclusive and connected urban environment, encouraging active participation and engagement among residents.
Reduced Traffic Pollution
A notable reduction in traffic pollution emerges as a compelling benefit of pedestrian-centric urban design. By prioritizing walkability, cities can effectively achieve traffic reduction, leading to fewer vehicles on the roads. This decrease in vehicular traffic directly correlates with improved air quality, as emissions from cars, trucks, and buses are markedly curtailed. The strategic integration of pedestrian-friendly roads and crosswalks encourages individuals to choose walking over driving, thereby reducing the dependency on fossil fuels. This shift not only diminishes greenhouse gas emissions but also paves the way for cleaner, healthier urban environments. In addition, pedestrian-centric designs promote sustainable urban living by fostering public transportation use and reducing the ecological footprint, thereby contributing to a visionary approach towards urban planning.
Case Studies: Successful Pedestrian Projects Around the World
Transformations in urban landscapes across the globe demonstrate the profound impact of pedestrian-friendly infrastructure on city life. Case studies of pedestrian projects highlight a universal trend toward prioritizing pedestrianization. In Copenhagen, Denmark, the conversion of Strøget into a car-free zone revitalized the city center, increasing foot traffic and boosting local commerce. Similarly, New York City’s Times Square pedestrianization project enhanced public space, decreasing vehicular congestion while promoting economic growth. In Seoul, South Korea, the Cheonggyecheon Stream restoration illustrates the environmental and social benefits of converting roadways into pedestrian areas. These projects underscore a collective vision for urban design that places pedestrians at the forefront, aiming to create vibrant, accessible, and sustainable urban environments that foster community and enhance quality of life.
Designing Streets for Safety and Accessibility
Building on the successes of pedestrian projects worldwide, effective street design is paramount to guarantee safety and accessibility for all. Central to this design ethos is the implementation of traffic calming measures which can greatly reduce vehicular speeds, thereby minimizing accident risks. Techniques such as raised crosswalks, curb extensions, and road narrowing are instrumental in fostering an environment conducive to pedestrian movement. Equally important is the strategic placement of road signage, which must be clear and visible to guide both drivers and pedestrians safely. Signage should inform, warn, and guide, enhancing the intuitive navigation of shared spaces. By meticulously integrating these elements, city planners can create streets that are not only safer but also more inclusive, ensuring accessibility for diverse populations.
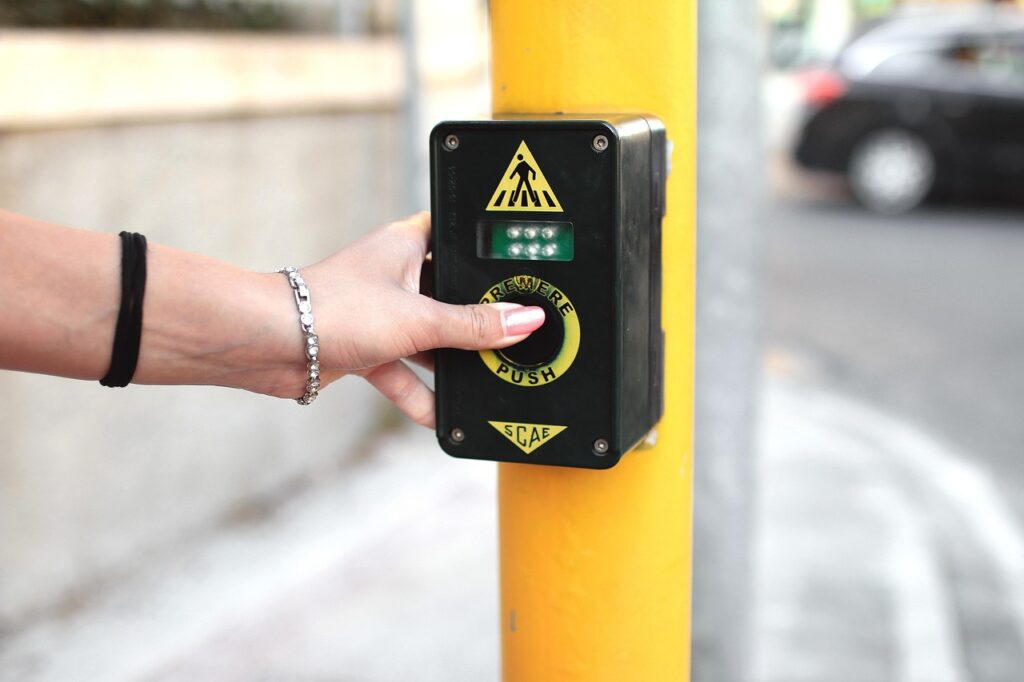

The Role of Technology in Enhancing Walkability
While the physical design of streets plays a crucial role in enhancing pedestrian safety, technology serves as a powerful catalyst in advancing walkability. Smart crosswalks, equipped with sensors and LED lights, adapt to real-time pedestrian flow, reducing accident risks and increasing visibility. These intelligent systems can communicate with traffic lights, optimizing signal timing based on pedestrian presence. In parallel, navigation apps are revolutionizing the pedestrian experience by providing real-time data on the safest and most efficient walking routes. These apps integrate information about foot traffic, crosswalk locations, and even temporary obstacles. Together, smart crosswalks and navigation apps create a synergy that not only enhances pedestrian safety but also encourages walking as a primary mode of transportation, fostering healthier, more connected communities.
Community Engagement and Public Input
To truly enhance pedestrian-friendly infrastructure, the integration of community engagement and public input is indispensable. A systematic approach to gathering community feedback guarantees that the needs and preferences of local residents are understood and addressed. Design workshops serve as a pivotal platform for stakeholders to collaboratively envision and refine proposals. These workshops facilitate a dialogue between urban planners, architects, and the community, guaranteeing alignment with pedestrian-centric goals. By analyzing diverse perspectives, planners can identify potential obstacles and innovative solutions. The data collected from these interactions can guide the prioritization of projects, guaranteeing resources are allocated efficiently. Ultimately, this participatory approach fosters a sense of ownership among residents, enhancing the success and sustainability of pedestrian-friendly initiatives.
Economic Impacts of Pedestrian-Friendly Environments
Community engagement not only enhances the alignment of pedestrian-friendly infrastructure with local needs but also reveals the potential economic benefits these environments can generate. When cities prioritize walkability, they often experience significant economic growth. Enhanced pedestrian areas attract businesses by increasing foot traffic, which can lead to higher retail sales and property values. Additionally, pedestrian-friendly zones contribute to urban revitalization, transforming neglected areas into vibrant community hubs. This urban transformation can attract tourists and new residents, further boosting the local economy. Furthermore, reduced reliance on vehicles can lower infrastructure maintenance costs and promote sustainable development. Investment in such environments aligns with long-term economic strategies, fostering communities that are not only economically viable but also socially and environmentally resilient.
Overcoming Challenges in Urban Planning
Despite the clear benefits of pedestrian-friendly environments, urban planning still faces significant challenges in their implementation. Zoning regulations, often outdated, can hinder the development of such spaces by prioritizing vehicular traffic over pedestrian pathways. Revising these regulations to align with modern urban needs is critical. Funding challenges also pose a considerable obstacle, as financial resources must be allocated strategically to support infrastructure improvements. Effective stakeholder collaboration is essential to navigate competing interests and guarantee thorough planning. Engaging public agencies, private developers, and community groups can foster innovative solutions. Additionally, transportation policies must be adapted to integrate pedestrian-focused designs, requiring a shift from car-centric frameworks. Addressing these challenges is fundamental for creating vibrant, sustainable urban environments that prioritize walkability.
The Future of Urban Mobility and Walkability
The future of urban mobility and walkability hinges on the integration of cutting-edge street design innovations that prioritize pedestrian safety and comfort. Promoting active transportation, such as walking and cycling, requires cities to implement extensive infrastructure that seamlessly connects communities. Furthermore, accessibility and inclusivity initiatives are essential to guarantee that urban environments are navigable and equitable for all individuals, regardless of physical ability.
Innovations in Street Design
Urban planners and architects are increasingly embracing a range of innovative street designs aimed at enhancing mobility and walkability in cities. A pivotal innovation is the integration of smart crosswalks, which employ sensors and LED lights to adapt to pedestrian traffic, ensuring safety and efficiency. These high-tech crosswalks can communicate with traffic signals, optimizing vehicle flow while prioritizing pedestrian movement. Simultaneously, incorporating urban greenery into street layouts not only beautifies the environment but also contributes to ecological benefits, such as reducing heat islands and improving air quality. Green corridors can serve as natural buffers between pedestrians and vehicles, creating a more pleasant walking experience. These forward-thinking designs represent a paradigm shift towards sustainable, pedestrian-centric urban landscapes, reflecting the future of urban mobility.
Promoting Active Transportation
As cities around the world face escalating challenges related to congestion and pollution, promoting active transportation emerges as an essential strategy in reshaping urban mobility. Encouraging active commuting, such as walking and cycling, reduces reliance on motor vehicles, thereby alleviating traffic congestion and decreasing harmful emissions. Pedestrian advocacy plays a significant role in this transformation by emphasizing the need for safe, accessible, and interconnected pathways. Urban planners and policymakers are increasingly investing in infrastructure that supports active transportation, including expanded sidewalks, bike lanes, and pedestrian-only zones. These efforts not only foster healthier lifestyles but also enhance community engagement and economic dynamism. By prioritizing pedestrian-friendly environments, cities can advance toward more sustainable and livable futures, aligning with global aspirations for greener urban spaces.
Accessibility and Inclusivity Initiatives
Accessibility stands as a cornerstone in the evolving landscape of urban mobility and walkability. As cities endeavor to enhance their pedestrian environments, universal design principles become paramount. These principles aim to create pathways and spaces that accommodate all individuals, regardless of physical ability. Inclusive infrastructure is vital, facilitating ease of movement for those with disabilities, the elderly, and families with young children. This includes features like tactile paving, audible signals, and widened sidewalks. Visionary urban planning now emphasizes seamless connectivity, integrating public transport systems with pedestrian routes to foster a cohesive network. By prioritizing accessibility, cities are not only improving functionality but are also promoting equity, ensuring that urban environments are welcoming and functional for all residents and visitors.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Are Pedestrian-Friendly Roads Impacting Local Businesses?
Pedestrian-friendly roads greatly increase foot traffic, fostering business growth. Improved accessibility attracts more customers, leading to higher sales. Businesses adapt by enhancing storefront appeal and expanding services, resulting in a sustainable economic environment and vibrant community engagement.
What Measures Ensure Pedestrian Safety During Road Construction?
During road construction, pedestrian safety is guaranteed through implementing temporary signage for clear navigation and constructing barriers to separate pedestrians from active construction zones. These measures minimize risk, guiding pedestrians safely while maintaining efficient construction progress.
How Do Pedestrian-Friendly Designs Affect Traffic Congestion?
Pedestrian-friendly designs can greatly influence traffic congestion by altering pedestrian behavior and improving traffic flow. These designs encourage safer, more efficient crossing, thereby reducing vehicle idle times and promoting smoother vehicular movement through better managed intersections.
What Are the Environmental Benefits of Increased Walkability?
The environmental benefits of increased walkability include a reduced carbon footprint due to lower vehicle emissions and enhanced urban biodiversity, as green spaces and pedestrian areas encourage diverse ecosystems and species to thrive in urban environments.
How Do Cities Fund Pedestrian Infrastructure Projects?
Cities fund pedestrian infrastructure projects through grant opportunities from federal and state programs, leveraging public-private partnerships to maximize resources. These methods guarantee sustainable development by integrating diverse financial inputs, fostering long-term urban planning and economic growth.