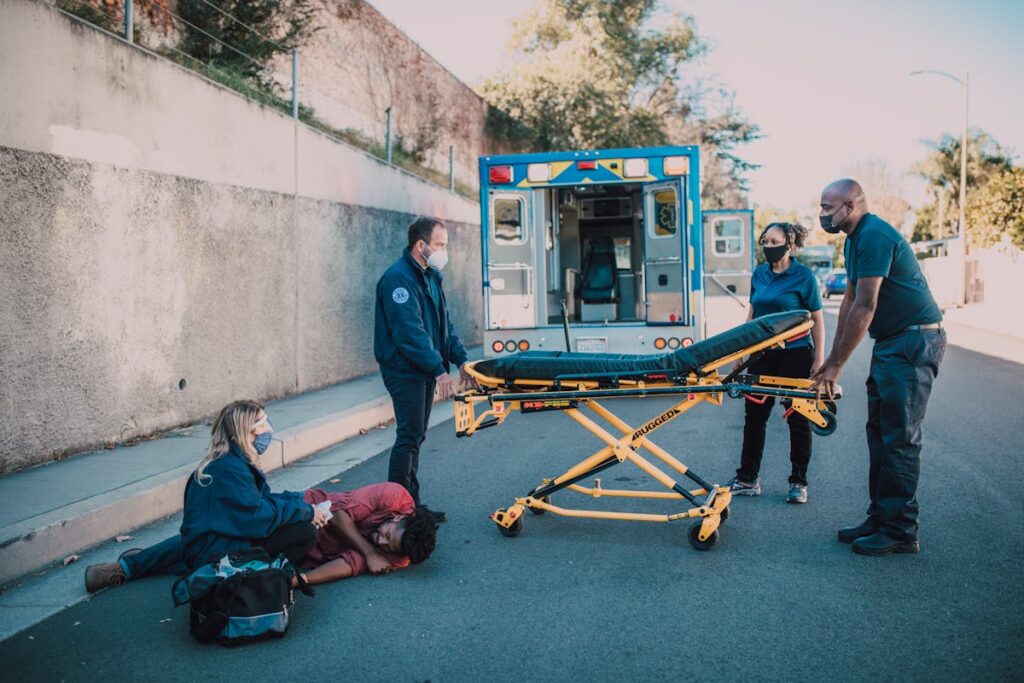
Emergency Medical Services (EMS) have undergone substantial evolution since their inception, rooted in military necessity during the Napoleonic Wars. Initial efforts focused on battlefield casualty stabilization, which informed modern pre-hospital care standards. This historical trajectory highlights significant advancements in ambulance technology, paramedic roles, and legislative oversight, ensuring consistent emergency response nationwide. Yet, as EMS confronts 21st-century challenges, its future remains a pivotal area of exploration, influencing healthcare delivery profoundly.
The Origins of Emergency Medical Services
Emergency Medical Services (EMS) trace their origins back to the Napoleonic Wars, where military physicians recognized the need for rapid medical attention on the battlefield. The concept of prehospital care emerged as a critical response to the high mortality rates among wounded soldiers. During this period, the principles of emergency training were developed to guarantee quick and efficient medical intervention. Physicians and medical personnel were trained to stabilize patients and perform essential medical procedures prior to hospital arrival. Evidence from historical accounts highlights how early EMS practices considerably reduced battlefield fatalities. The evolution of these methods laid the groundwork for modern prehospital care systems, underscoring the importance of timely and effective medical response in emergency situations. Clinical expertise and concise communication remain central to EMS today.
The Role of Military Innovations in EMS Development
Military innovations have profoundly influenced the development of Emergency Medical Services (EMS) systems. Techniques such as military triage, initially designed for battlefield medicine, have been adapted to prioritize treatment in civilian emergencies. The principles of military triage allow EMS to effectively manage mass casualty incidents by categorizing patients based on the urgency of their needs. Battlefield medicine has also contributed considerably to advancements in trauma care, enabling EMS to deliver critical interventions promptly. In addition, military rescue operations have informed the strategic planning and execution of civilian rescue missions. Medical logistics, honed in military settings, guarantees efficient resource allocation and supply chain management in EMS scenarios. Rapid response strategies, derived from military protocols, enhance the effectiveness and speed of EMS interventions in critical situations.
The Advent of Modern Ambulance Services
As medical knowledge and transportation technologies evolved, the advent of modern ambulance services marked a pivotal shift in emergency medical care. The integration of advanced ambulance technology greatly enhanced the efficiency and effectiveness of patient transport. Modern ambulances became equipped with life-saving medical equipment, facilitating on-site interventions that were previously impossible. This evolution paralleled the rise of skilled paramedics, whose expanded roles included advanced life support, thereby transforming pre-hospital care. The paramedic evolution underscored the importance of rapid response and specialized training, leading to improved patient outcomes. Advances in ambulance technology and paramedic training collectively established a robust framework for contemporary EMS, ensuring timely and proficient emergency medical interventions. This transformation was instrumental in setting new standards for emergency care delivery.
The Impact of Legislation on EMS Systems
Legislation has played a pivotal role in shaping EMS systems by establishing key milestones that have standardized emergency medical care. Funding and resource allocation are directly influenced by these legislative frameworks, ensuring that EMS systems can maintain operational efficiency and effectiveness. Evidence indicates that such regulatory measures have improved patient outcomes by facilitating access to necessary resources and training.
Key Legislative Milestones
Despite the complexities involved, the evolution of Emergency Medical Services (EMS) has been considerably shaped by key legislative milestones. Legislative frameworks have provided the foundation for structured emergency response systems. The Highway Safety Act of 1966 marked a pivotal shift, mandating states to develop EMS systems, thereby revolutionizing pre-hospital care. The Emergency Medical Services Systems Act of 1973 further established federal funding mechanisms to standardize EMS practices, ensuring cohesive response capabilities. Legislative initiatives have consistently aimed at enhancing patient outcomes through structured protocols and training requirements. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) played a critical role in formalizing EMS education and certification standards. Evidence suggests that these legislative milestones have considerably improved the efficacy and reliability of emergency medical response nationwide.
Funding and Resource Allocation
While legislative milestones have undeniably shaped the structure of Emergency Medical Services (EMS), the impact on funding and resource allocation is equally critical to their effectiveness. Sustainable funding models are essential to maintain high-quality EMS operations. Legislation influences financial strategies by setting guidelines for federal, state, and local contributions. Effective resource allocation guarantees readiness and rapid response, directly affecting patient outcomes. Evidence suggests that regions with well-structured funding experience enhanced service delivery, including advanced training and updated technology. Conversely, inadequate funding often results in resource scarcity, impacting response times and care quality. Policymakers must prioritize sustainable funding to address disparities and optimize EMS systems. Continuous evaluation is necessary to align legislative actions with evolving EMS needs and technological advancements.
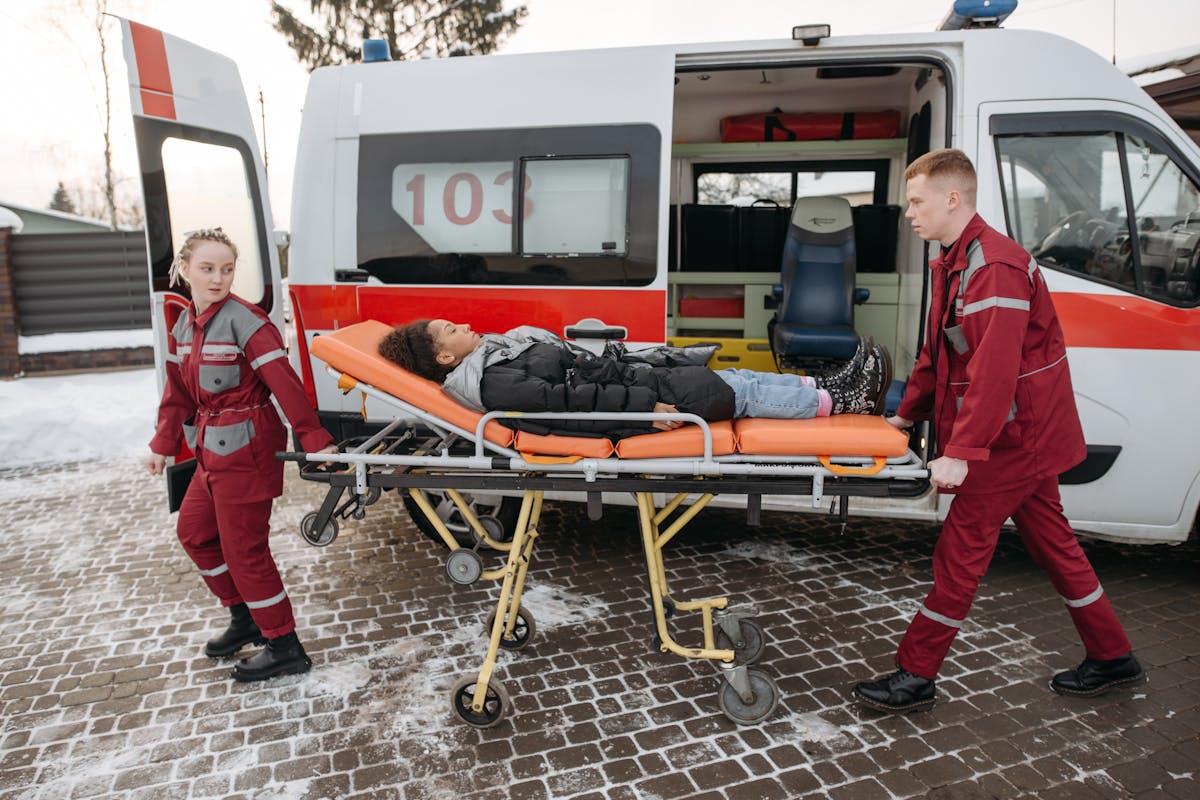

Technological Advancements in Emergency Care
Technological advancements in emergency care have considerably enhanced the capabilities of EMS providers through innovative life-saving devices and the integration of telemedicine in ambulances. Devices such as automated external defibrillators (AEDs) and portable ventilators have improved on-site intervention outcomes. Concurrently, telemedicine enables real-time communication with specialists, allowing for expert guidance and immediate decision-making in critical situations.
Innovative Life-Saving Devices
In recent years, numerous groundbreaking devices have emerged, transforming the landscape of emergency medical services and enhancing patient outcomes. Wearable defibrillators have become pivotal in delivering timely intervention for patients at risk of sudden cardiac arrest. These devices continuously monitor heart rhythms, providing immediate defibrillation when necessary, thereby reducing mortality rates. Additionally, automated CPR machines have revolutionized resuscitation efforts. These devices guarantee consistent, high-quality chest compressions, a critical factor in improving survival rates during cardiac emergencies. Automated CPR minimizes human error and fatigue, maintaining ideal compression depth and rate. Both wearable defibrillators and automated CPR represent significant technological advancements in pre-hospital care, offering evidence-based solutions that enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of emergency medical interventions.
Telemedicine in Ambulances
A growing number of emergency medical services are integrating telemedicine into ambulances, marking a significant advancement in pre-hospital care. This integration facilitates remote consultations, enabling paramedics to connect with emergency physicians in real-time. By leveraging telecommunication technologies, paramedics can transmit crucial patient data, enhancing the decision-making process and ensuring timely interventions. Telemedicine in ambulances allows for continuous patient monitoring, offering health professionals the ability to assess and adjust treatments based on real-time data. Studies indicate that such practices can improve patient outcomes by reducing the time to definitive care. Additionally, telemedicine has the potential to optimize resource utilization, ensuring that patients receive appropriate care levels en route to medical facilities. Therefore, telemedicine represents a pivotal evolution in emergency medical services.
The Evolution of EMS Training and Certification
While advances in medical knowledge continually shape healthcare practices, the evolution of EMS training and certification reflects these changes by adapting to new challenges and technologies. Training programs increasingly incorporate simulation training, a method proven to enhance the readiness of emergency personnel by providing realistic scenarios without patient risk. These simulations allow practitioners to hone critical decision-making skills in controlled environments. Certification standards have also evolved, becoming more rigorous and aligned with the latest medical guidelines to guarantee competency and quality of care. Evidence supports that higher certification standards contribute to improved patient outcomes. Regular updates to curricula and certification processes are imperative to maintain a workforce capable of responding effectively to emergencies, guaranteeing public safety remains paramount in EMS operations.
Integration of EMS With Healthcare Systems
As healthcare systems continue to evolve, the integration of Emergency Medical Services (EMS) within these systems becomes increasingly essential. This integration guarantees timely and efficient care through collaborative partnerships between EMS providers and healthcare facilities. An integrated response involves the seamless coordination of pre-hospital and in-hospital care, optimizing patient outcomes. Evidence demonstrates that such integration reduces response times, improves resource allocation, and enhances communication across medical teams. Collaborative partnerships facilitate shared protocols and data exchange, aligning EMS with broader healthcare objectives. By embedding EMS into the healthcare continuum, systems can guarantee continuity of care from the point of emergency to recovery. This approach not only elevates patient care standards but also strengthens the healthcare system’s overall resilience and adaptability.
Challenges Facing EMS in the 21st Century
The complexity of modern healthcare presents significant challenges for Emergency Medical Services (EMS) in the 21st century. Staffing shortages strain resources, leading to increased response times and impacting patient outcomes. Funding challenges hinder the adoption of advanced technology, limiting efficiency and effectiveness. Regulatory barriers further complicate operations, delaying necessary improvements. Public awareness of EMS roles and capabilities remains inadequate, hindering community engagement and support. Mental health issues, both among EMS personnel and in the populations they serve, require specialized approaches often not adequately addressed. Effective community engagement is vital in educating the public and improving service delivery. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted strategy that emphasizes innovation, collaboration, and an evidence-based approach to enhance EMS resilience and responsiveness.
The Future of Emergency Medical Services
Addressing the challenges faced by Emergency Medical Services requires a forward-thinking perspective to secure their future effectiveness. Integrating predictive analytics into EMS can enhance decision-making by anticipating demand patterns and resource allocation needs. Predictive models based on historical data can optimize response times and improve patient outcomes. Moreover, community engagement is vital. By fostering partnerships with local organizations and stakeholders, EMS can tailor services to meet specific community health needs, ensuring a more responsive and efficient system. Training EMS personnel in the use of advanced analytics tools and community-based strategies will be pivotal. As EMS systems evolve, a fusion of technology and community collaboration will be essential to meet the growing demands of emergency medical care, enhancing overall system resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Most Common Types of Emergencies Handled by EMS?
The most common emergencies managed include cardiac arrest and trauma cases. These incidents require rapid intervention, where evidence-based protocols guide clinical decisions to stabilize patients, minimize harm, and improve survival outcomes in high-pressure, time-sensitive situations.
How Are EMS Services Funded and Who Oversees Them?
EMS services are funded through diverse sources, including government allocations, insurance reimbursements, and grants. Oversight agencies, such as local health departments and federal bodies, guarantee compliance with standards and regulations, maintaining operational efficacy and service quality.
How Do EMS Personnel Prioritize Calls During High-Demand Periods?
During high-demand periods, EMS personnel utilize call triage systems to prioritize emergencies, ensuring resource allocation aligns with patient needs based on urgency. Evidence-based protocols guide decision-making to maximize efficiency and patient outcomes under clinical expertise.
What Kind of Vehicles Are Used in EMS Besides Ambulances?
In EMS, vehicles beyond ambulances include bicycle medics for rapid urban response and rescue boats for water-based emergencies. These alternatives enhance operational efficiency, ensuring timely medical care delivery in diverse environments, backed by evidence-based deployment strategies.
How Are Rural EMS Services Different From Urban Ones?
Rural EMS services face challenges like long response times and limited personnel, whereas urban EMS benefits from greater resources, including advanced medical facilities and personnel. These differences profoundly impact patient outcomes and require tailored operational strategies.